(July 15, 2022) Oblivious to his nomination, Professor Suresh Bhargava was sitting in his office when he received a letter informing him that he was being conferred with the Queen’s Birthday 2022 honour – Member of the Order of Australia (AM). Though his initial reaction was that of surprise, the academician also felt extremely excited to be honoured by the Queen. “I have received numerous awards for my scientific research. However, this one was for my contribution to the betterment of my community,” shares Professor Bhargava, as he connects over a call from Melbourne. “It is incredible when people recognise your contributions that created a positive difference. I was thrilled that my adopted country valued my three decades of hard work.”

Professor Suresh Bhargava was conferred with the Queen’s Birthday 2022 honour – Member of the Order of Australia (AM)
A professor at esteemed Universities in six countries, the academician is a winner of several awards, including the most prestigious award in engineering, the ‘CHEMECA medal’. “I am happy and honoured that I can train the next generation of scientists,” shares the professor, as he talks about his 30 years in academia with Global Indian.
Academically inclined
Hailing from Meerut in Uttar Pradesh, Professor Bhargava’s father worked as a station master in the Indian Railways. Growing up in a middle-class family, the young academician was keen to do better at studies. “I was a bright student and my teachers encouraged me a lot. It was one of my school teachers who first introduced me to Chemistry,” share the academician.
Having discovered the world of elements and chemicals at an early age, Professor Bhargava was completely fascinated by Chemistry’s contribution to everyday life of an average man. “I realised that almost everything around us is somehow related to Chemistry. When we are very happy or sad, we tend to cry – which is nothing but a chemical reaction. Similarly, when we are stressed, it is again a chemical reaction in the brain. I am a scientist now and know much more than what I did as a young student – but Chemistry still fascinates me,” he smiles.

The sudden death of his father due to an accident left the family shattered. Still pursuing his master’s, the idea of leaving his studies and taking up a full-time job did cross his mind. But it was his teachers who convinced his mother to let him carry on with his studies. “They took care of all the expenses,” shares the academician, who topped his university that year.
Road to the UK
Upon finishing his master’s, he became a lecturer at the young age of 19. Interestingly though, the esteemed academician of today had other ambitions as a young man. “When I was a kid, I dreamt of becoming a pilot someday. I cleared the Services Selection Board (SSB) examination to join the Indian Air Force. However, my family believed that I should not join the armed forces, and so I didn’t go,” he reminisces.
As he started taking classes, he realised that most of his students were his age. “So rather than becoming their teacher, I decided to teach them as a friend. And I was a very popular professor,” he laughs. However, his destiny was yet to reveal some interesting plans.

Professor Bhargava being conferred with NRI of the Year award, 2017
Recalling one of the happiest moments of his life, Professor Bhargava says, “It was on May 15, 1979, when I received a letter from the British Council announcing that my application to do a PhD in the UK had been approved.” The British Council offered to place him under a very esteemed English scientist and former president of the Royal Society of Chemistry, Professor Eddie Abel, and pay him a handsome salary. “It felt like all my prayers were answered,” shares the academician, who started his PhD programme at the University of Exeter the same year.
While most people take five years to finish their PhD, he finished his research work in just three years. “Professor Abel was very impressed with my work, which was published in various scientific journals. When it was time for me to leave for India, he asked me to stay back. However, I had a contract with the University Grant Commission, and I had to return,” shares the professor.
Land Down Under
Although he returned to India and rejoined his university, he knew he was meant for greater things. “My university management also encouraged me and I left for the UK again. My mentor spoke to his peers at the Australian National University and that is how I landed in Canberra in 1983,” shares the chemistry scientist.
Australia became his new home. With ground-breaking research work and 500 authored/co-authored journal articles, he made a splash in the new country. His research and scientific insights not just aided the big companies, but even helped governments solve many issues. In 1990, he joined the Royal Melbourne Institute of Technology (RMIT) and established the Centre for Advanced Materials and Industrial Chemistry (CAMIC), a state-of-the-art research centre.
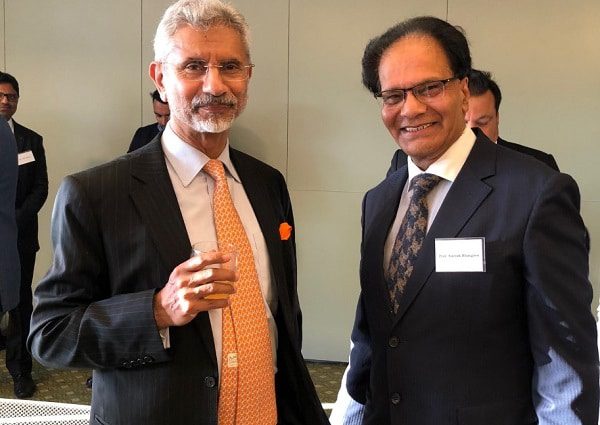

Professor Bhargava with S Jaishankar, Minister of External Affairs of India
For his research, Professor Bhargava holds 12 patents, including one for gold-based metallodrug for cancer treatment. “When my mother was very ill, she only took ayurvedic medicines. One of her medicines was swarna bhasma, which is gold ash. That got me thinking about how metals affect the human body, and I started my research on how gold can be used as a medicine. We found that gold was about 200 percent better for cancer treatment than the drugs which are currently used. I am still working on the research to develop the medicine,” he explains.
Living by the principle that his research should contribute to enhancing the environment, the professor also developed a nanotechnology mercury sensor to monitor the toxic smoke emission from refineries for industrial use.
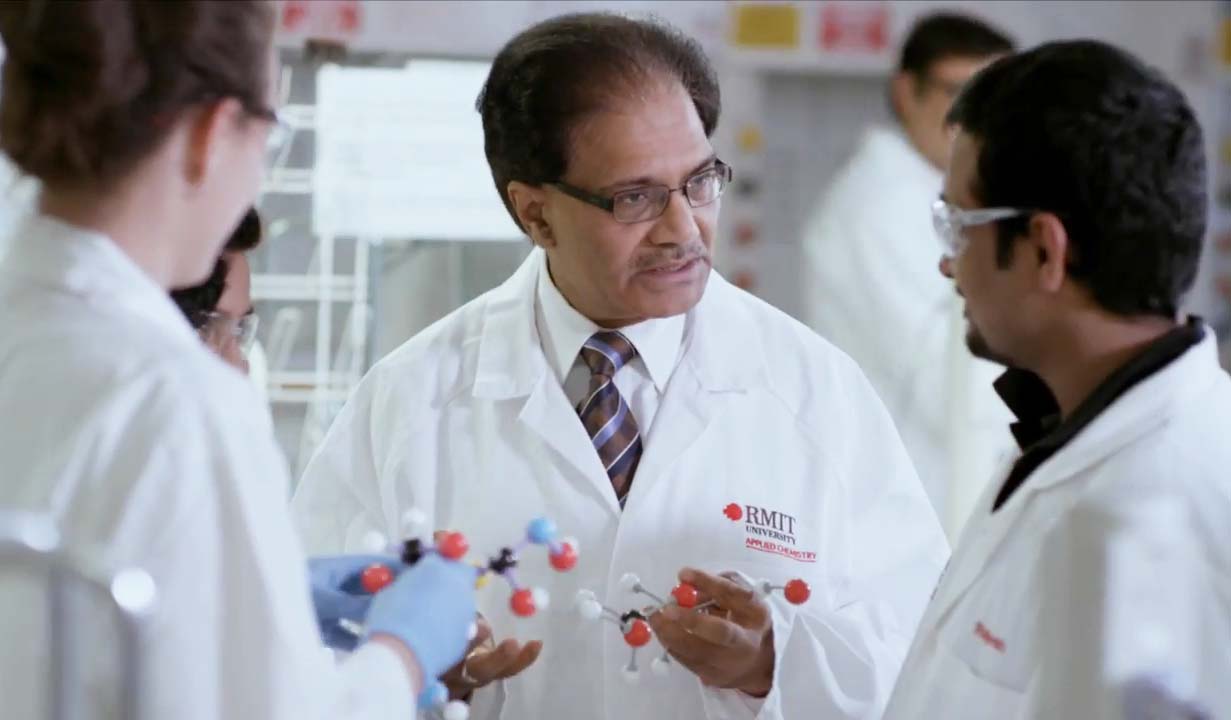
In a career spanning over 30 years, Professor Bhargava has supervised more than 60 PhDs. His teaching methods don’t just help his students excel in academics, but also make them industry-ready. A living bridge between India and Australia, the professor was conferred the PC Ray Chair by the Indian National Science Academy in 2014. He recently developed an award-winning PhD programme that connects laboratories of the Indian Council of Scientific & Industrial Research (CSIR) with RMIT, giving the PhD scholars in India a platform for high-quality research.
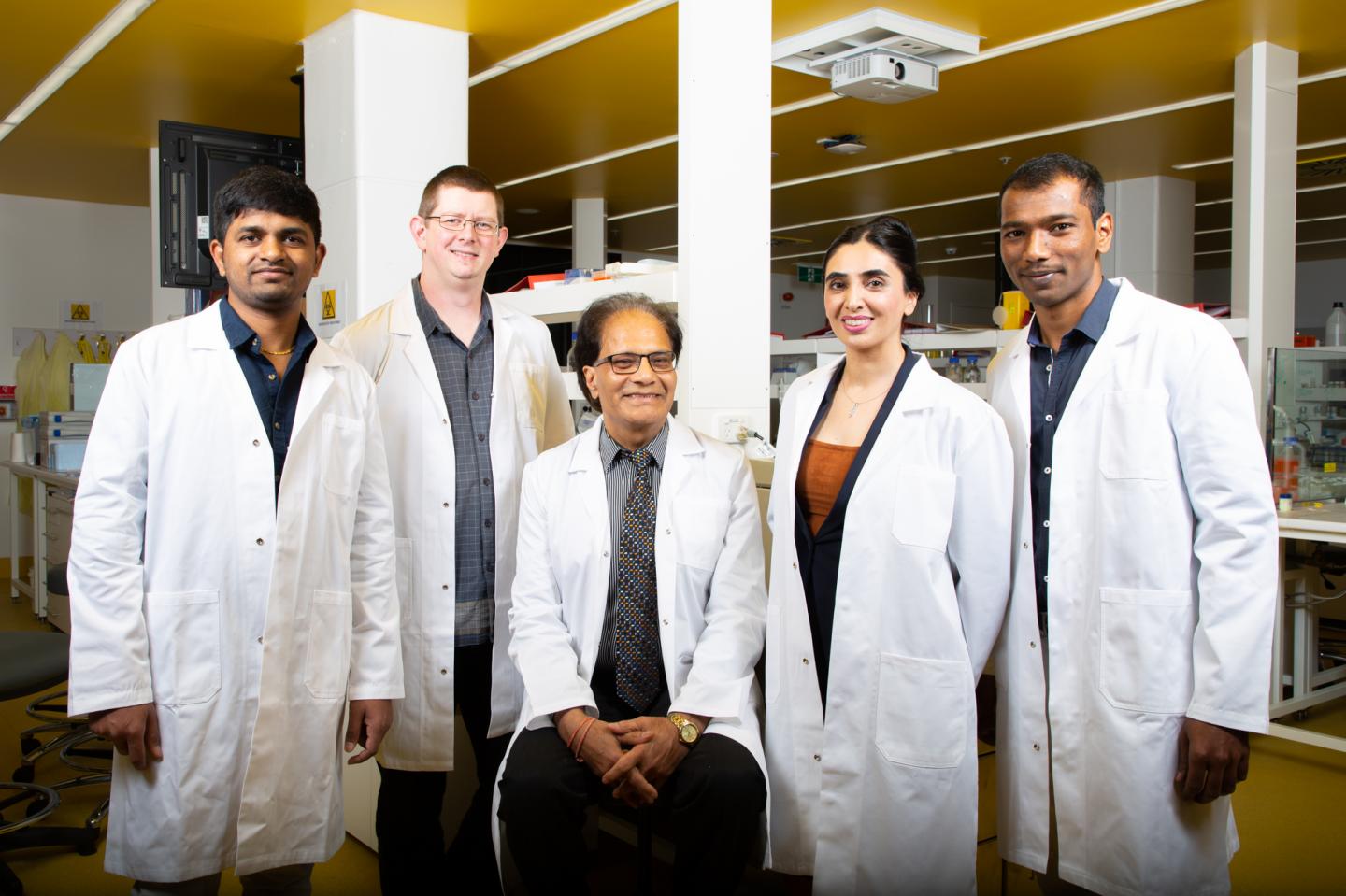

Professor Bhargava with the molecular engineering group at RMIT
“A career in academics gives you a unique platform. You meet new students every year, but at the same time, it gives you a chance to work on many research works. As a professor, I have always tried to teach my students how they can become innovators and use their research to better the lives of people and the planet itself,” shares the professor, adding, “In Indian philosophy, we use the term guru for someone who helps his disciples with all-round development. I am aiming to be a guru for my students.”
- Follow Professor Suresh Bhargava on LinkedIn
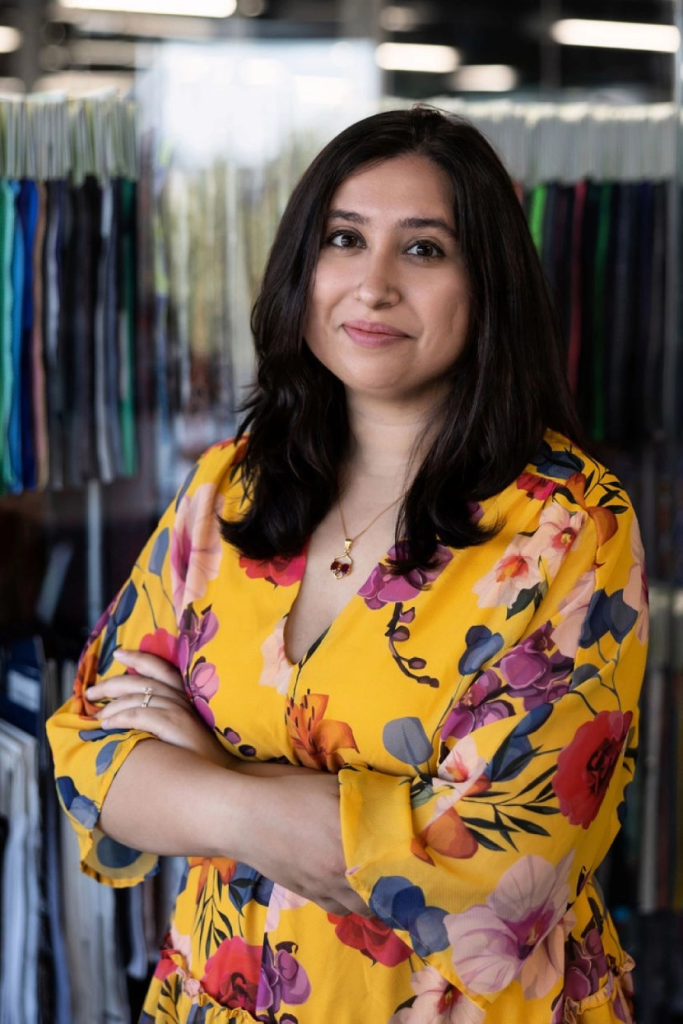


 Sarika Bajaj, CEO and co-founder, Refiberd[/caption]
Sarika Bajaj, CEO and co-founder, Refiberd[/caption]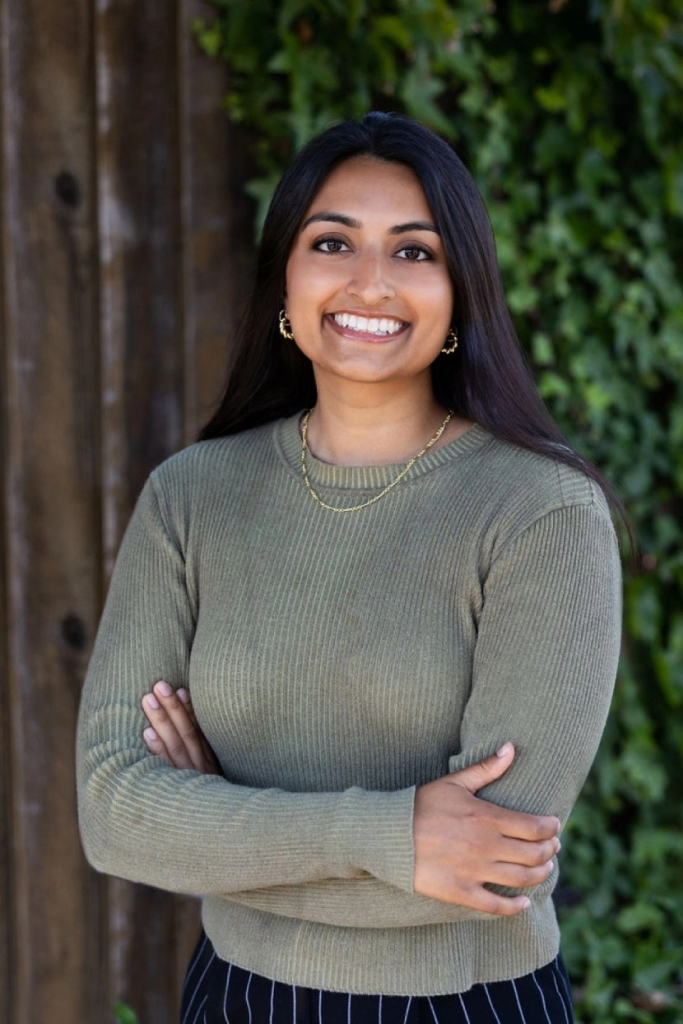 Tushita Gupta, CTO and co-founder, Refiberd[/caption]
Tushita Gupta, CTO and co-founder, Refiberd[/caption]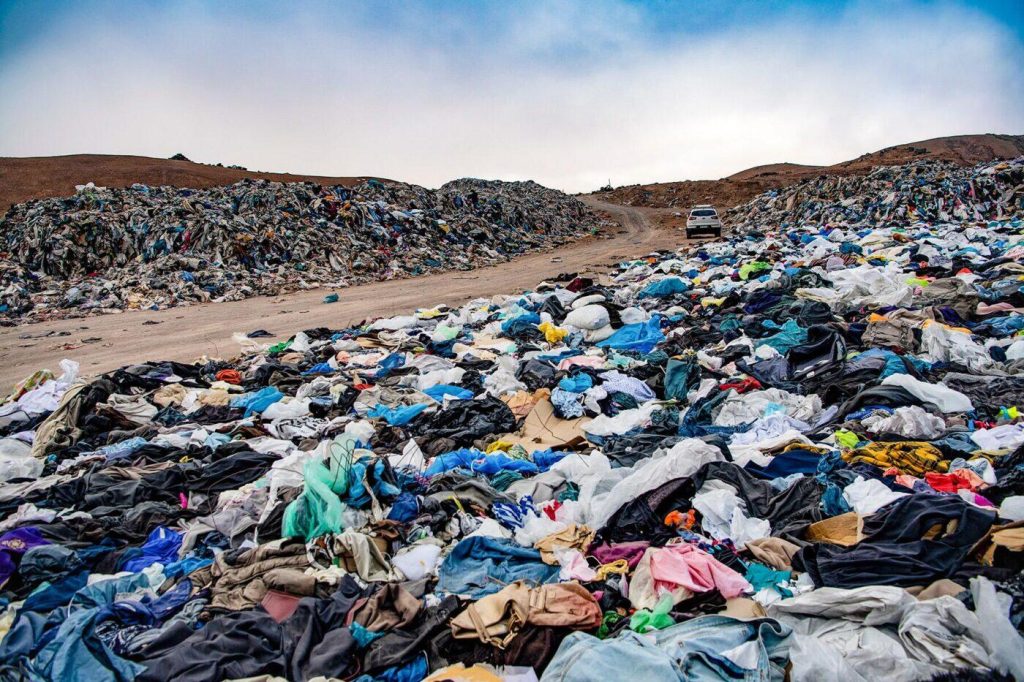 The clothing dump for fast fashion in the Atacama Desert, Chile[/caption]
The clothing dump for fast fashion in the Atacama Desert, Chile[/caption]
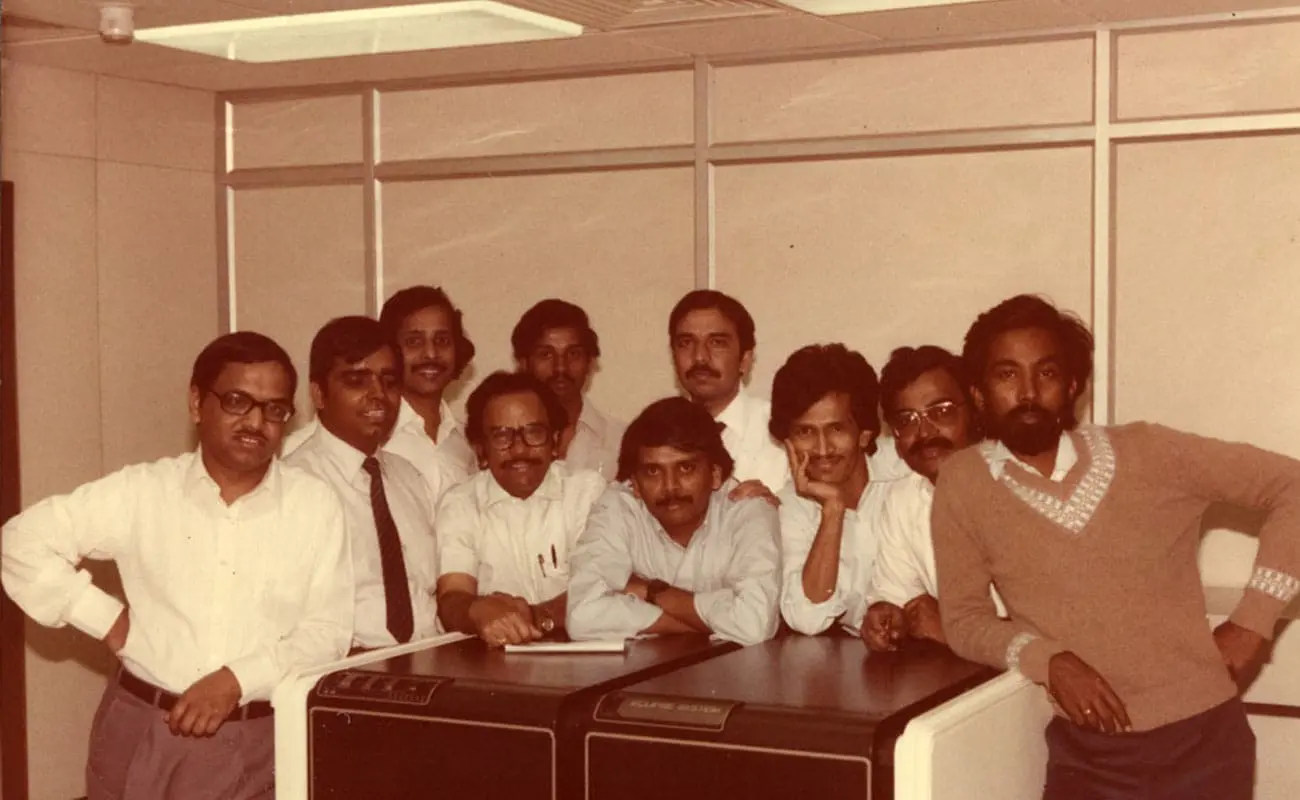 The co-founders of Infosys[/caption]
The co-founders of Infosys[/caption]



 Prafulla wth Dr Abdul Kalam after winning the National Talent Search Scholarship[/caption]
Prafulla wth Dr Abdul Kalam after winning the National Talent Search Scholarship[/caption] Prafulla during his student days in the U.S.[/caption]
Prafulla during his student days in the U.S.[/caption]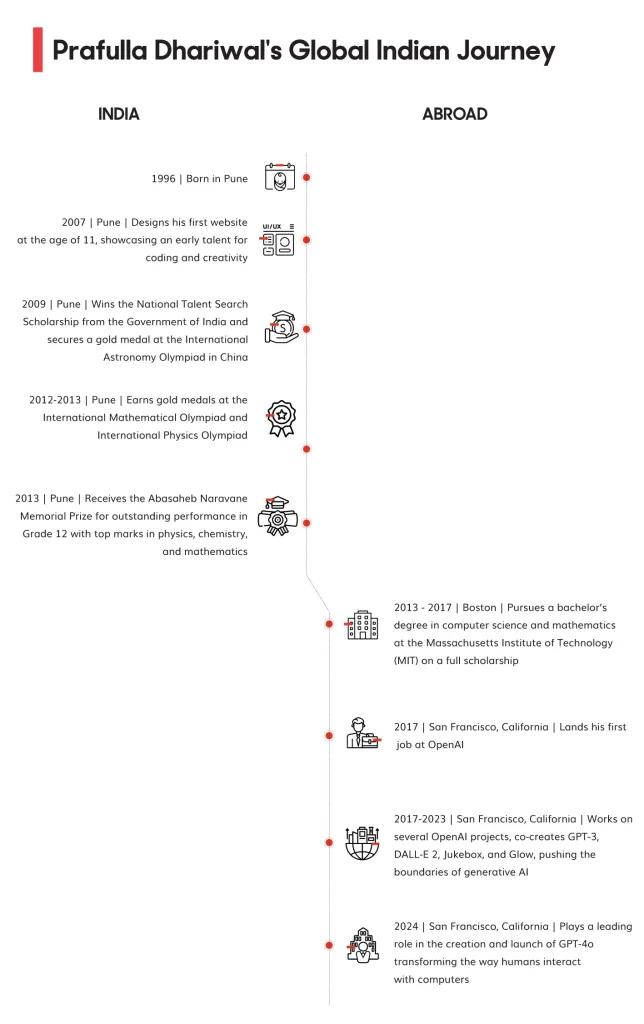
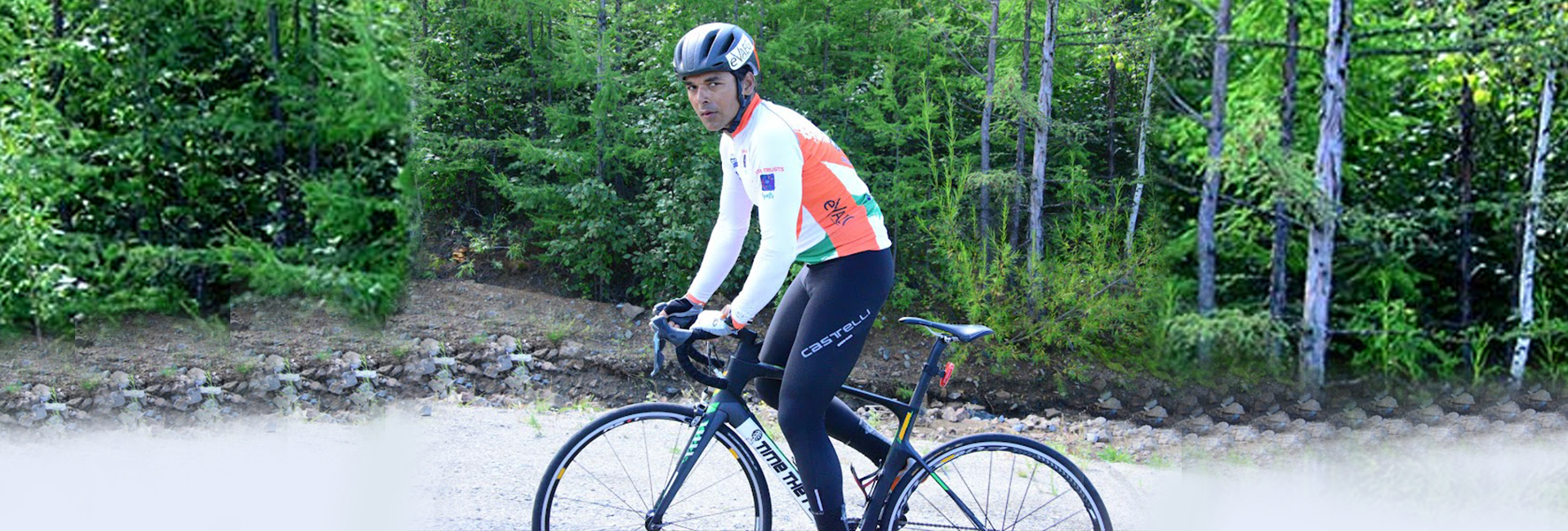
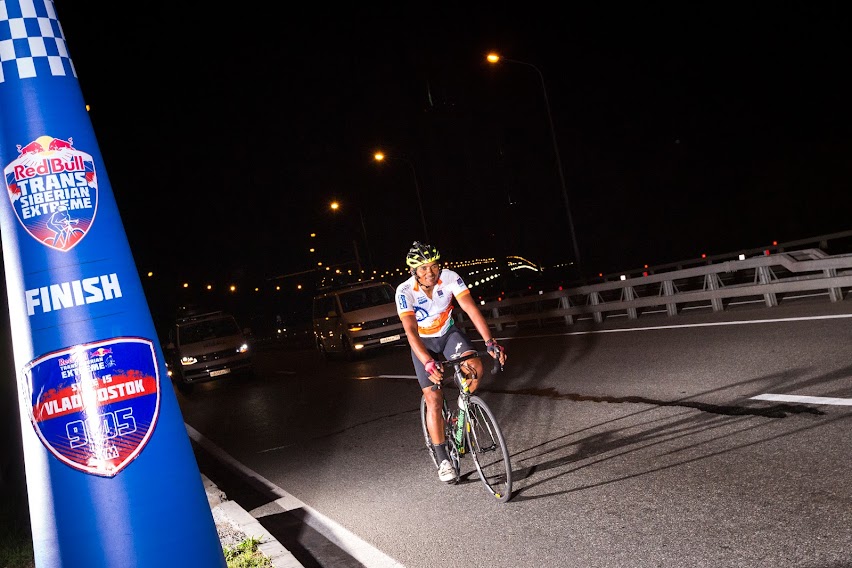

 Amit Samarth during the 15th stage (Khabarovsk - Vladivostok) of the Red Bull Trans-Siberian Extreme, on August 17, 2018[/caption]
Amit Samarth during the 15th stage (Khabarovsk - Vladivostok) of the Red Bull Trans-Siberian Extreme, on August 17, 2018[/caption]

